Category: Management
(53 von 100)
Why: I need to survive my business cash crisis.
Goal: Learn cash flow management.
Table of Contents
Action: Stretch payables, accelerate receivables, and minimize inventory.
3 Key Concepts
Summary
How to stretch payables, accelerate receivables, and minimize inventory?
You must have a plan. And here is how.

First, know your role as a business own in cashflow management.
- Cash finder – there is enough capital to pay all bills.
- Cash planner – forecast cash inflows and outflows.
- Cash distributor – pay bill according to the priority and timing.
- Cash collector – make customers pay on time.
“Get the cash in the door as fast as you can.” - Cash conserving – maximize value by avoiding immediate expenditures.
“Pay people as late as possible.”
Cash is the most important yet least productive asset that a small business owns.
Cash Management
It permits the owner to adequately meet the business’s cash demands, avoid retaining unnecessarily large cash balances, and stretch the profit-generating power of each dollar the business owns.
What is the problem with fast growth?
New business owners tend to focus heavily on sales at the beginning and realize almost always too late the following fact:
“It takes extra cash to support extra sales”
Therefore, rapid growth will induce immediately fixed cost increases like material cost and inventory. And double down the effect as cash collections fall behind.
Result: Cash Shortages
How to resolve cash shortages?
One must understand that cash is not profit. Although the business must have the cash to pay the bills at any point in time, profit is generated only after customers pay.
[Formula]
Extra cash required =
[(New sales – Gross profit + Extra overhead)
x
(Average collection period x 1.20*)]
/ Time frame for adding new sales
*The extra 20% is a cushion.
Cash Flow Cycle
The time lag between paying suppliers for merchandise or materials and receiving payment from customers for the product or service.
Cash cycle = difference between {Pay invoice and Customer pays)
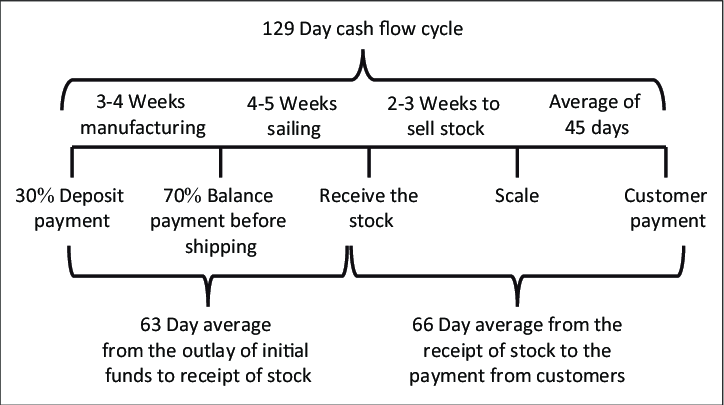
So now it is clear to see, profitability does not guarantee liquidity.
Profits are tied up in many forms like inventory or machinery.
Cash is the money that flows through a business in the cycle without being tied up in any other asset.
You pay creditors, employees, the government, lenders in CASH, not in PROFITS.
To sum up, we need to know where how the cash flow through our business. Therefore, make a plan for inflows and outflows is a must to avoid a cash crisis. Better: make a forecast.
It is unrealistic to trace every dollar. Therefore, you should focus mainly on the following Big Three cashflow problem causes.
- Accounts receivable
- Accounts payable
- Inventory
A firm should always try to accelerate its receivables and to stretch out its payables. And avoid excessive stock of inventory as it ties up valuable cash.
Goal check: I learned where to pay attention in cash flow management to avoid cash shortages.
Wasu’s Review
( 5.0 / 5.0 )
Get this book on Amazon here!


Pingback: Starting a Marketing Agency for Healthcare Business - Wasu Mekniran